Can a linear actuator encounter a hard stop?
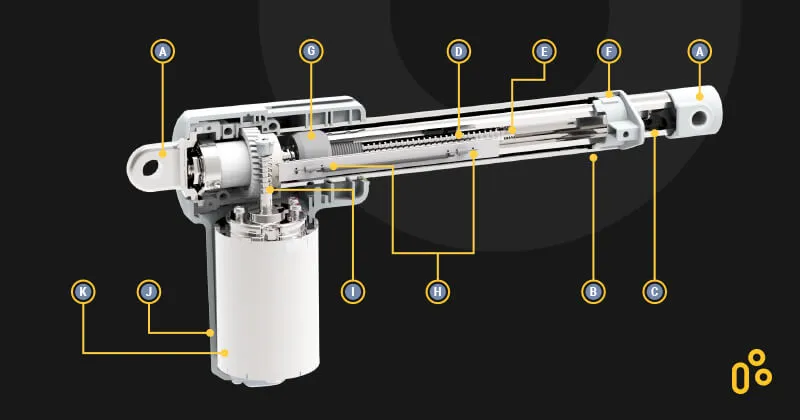
- Safety Considerations: Hard stops can play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and longevity of a linear actuator. By preventing the actuator from exerting excessive force or attempting to move beyond its mechanical limits, hard stops help protect the actuator from damage and potential failure. They also help prevent damage to the load or the surrounding equipment.
- Mechanical Limitations: Linear actuators have physical limits to their travel, which are determined by factors such as the length of the actuator's screw or rod, the size of the housing, and the presence of any built-in stops. These mechanical limitations define the maximum extension and retraction distances of the actuator. When the actuator reaches these limits, it encounters a hard stop.
- Limit Switches and Position Sensors: Many linear actuators are equipped with limit switches or position sensors. These devices are typically integrated into the actuator's design and can detect when the actuator reaches its end points. Once the actuator reaches a limit, the limit switch or position sensor sends a signal to the actuator's control system, indicating that it should stop further movement in that direction. This helps ensure precise control and prevents damage caused by continued actuator operation against hard stops.
- Adjustable Stops: In some cases, the hard stops in a linear actuator can be adjustable. This allows for customization of the actuator's travel limits according to the specific requirements of the application. Adjustable stops can be useful when fine-tuning the actuator's stroke length or when needing to limit the range of movement for safety or operational reasons.
- Overload Protection: Some linear actuators are equipped with overload protection mechanisms. These mechanisms can detect excessive force or torque exerted by the actuator and automatically shut down or limit the actuator's operation to prevent damage. Overload protection can be particularly useful when unexpected external forces or obstructions are encountered, reducing the risk of motor burnout or actuator failure.
It's important to note that the presence and functionality of hard stops, limit switches, position sensors, and other safety features can vary depending on the specific model and manufacturer of the linear actuator. Therefore, it is always recommended to refer to the product documentation and guidelines provided by the manufacturer to fully understand the capabilities, limitations, and safety considerations of a particular linear actuator.

 2024-08-30 16:01:40
Engineering
2024-08-30 16:01:40
Engineering
 2024-07-26 14:09:13
Engineering
2024-07-26 14:09:13
Engineering
 2024-07-18 09:42:00
Engineering
2024-07-18 09:42:00
Engineering