- +86 19149417743
- Zhengzhou, Henan Province, China
- Mon-fri: 8am - 7pm
Get a quote
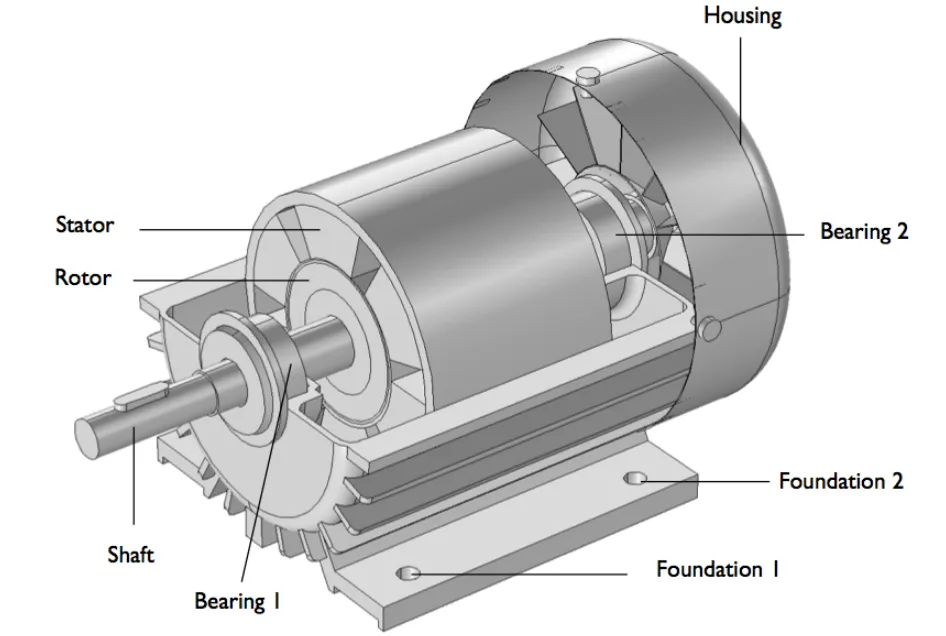
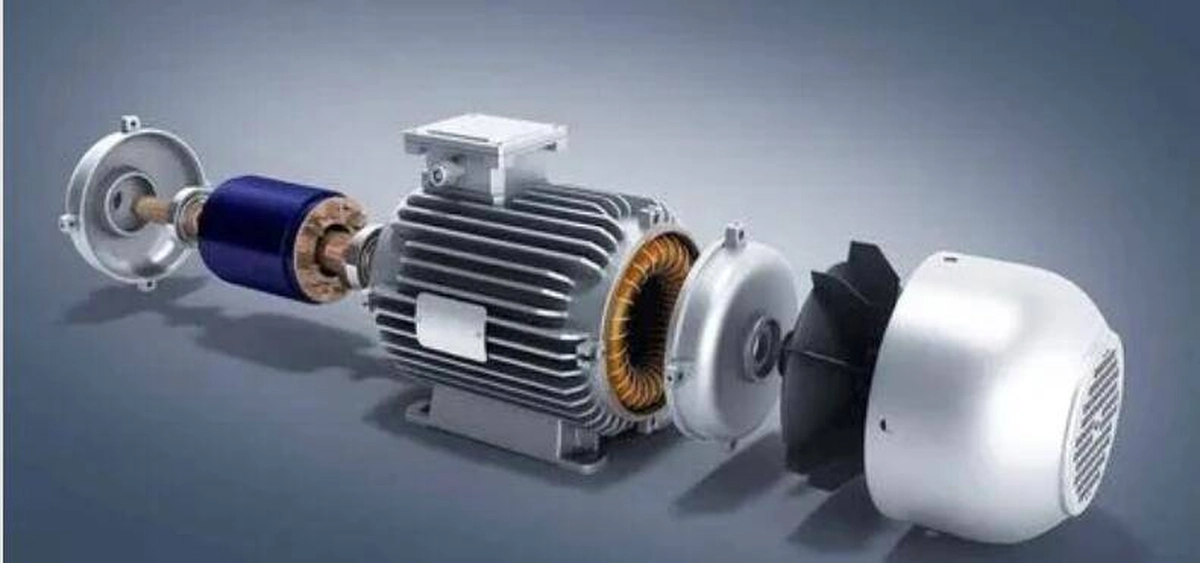
An induction motor is an electric motor that produces torque between a rotor and a stator by inducing electric current. Its basic working principle is that according to the law of electromagnetic induction, the alternating magnetic field generates an induced current in the stator coil, causing a rotating magnetic field to be generated in the rotor, thereby generating torque and driving the motor to rotate.
lunyee Induction motors usually consist of two parts: a stator and a rotor. The stator is the stationary part of the motor and consists of the stator core, windings, end covers, etc. There are three-phase interleaved winding coils distributed in the winding. When the three-phase power supply is connected to the winding, a rotating magnetic field will be formed in the winding.
The rotor is the rotating part of the motor, usually consisting of a rotor core and conductor bars. The conductor bars of the rotor are usually made of good conductive materials such as aluminum and copper and are fixed on the rotor core. When the rotating magnetic field passes through the rotor conductor bars, the induced electromotive force will generate current in the conductor bars because the current in the conductor bars will Under the action of electromagnetic force, the rotor will be subject to a certain torque.
According to the way the magnetic field is generated, induction motors can be divided into two types, namely asynchronous motors and synchronous motors. An asynchronous motor is the most common type of induction motor, and its rotor rotates at a speed slightly slower than the magnetic field, which is called slip. A synchronous motor is a motor whose rotation speed is exactly the same as the rotation speed of the magnetic field.
In short, the basic working principle of an induction motor is to form a rotating magnetic field in the stator coil through the principle of electromagnetic induction, thereby generating a rotating magnetic field in the rotor. The torque generated by the induced current drives the motor to rotate. This kind of motor has the advantages of simple structure, high reliability and stable operation. It is one of the main types of motors widely used in various industrial and civil fields.
The working method of an induction motor is based on the law of electromagnetic induction, using a rotating magnetic field to generate an induced current in the rotor, thereby causing the rotor to rotate and drive the load to move.
Induction motors usually consist of two parts: a stator and a rotor. The stator is the stationary part of the motor and consists of the stator core, windings, end covers, etc. There are three-phase interleaved winding coils distributed in the winding. When the three-phase power supply is connected to the winding, a rotating magnetic field will be formed in the winding.
The rotor is the rotating part of the motor, usually consisting of a rotor core and conductor bars. The conductor strips of the rotor are usually made of good conductive materials such as aluminum and copper and are fixed on the rotor core. When AC power is supplied to the stator winding, a rotating magnetic field will be generated in the winding. The rotating magnetic field will pass through the rotor core and induce the electromotive force in the conductor bar. Because the resistance within the conductor strip is non-zero, a current flows through the conductor strip. The direction of these currents is opposite to the direction of the rotor magnetic field, so they interact with the rotating magnetic field to produce torque. The direction of rotation of the rotor is the same as that of the rotating magnetic field, so the relative speed between them is very small.
Due to the presence of induced current in the rotor, lunyee induction motors are also called asynchronous motors because the rotation speed of the rotor is slightly lower than the speed of the rotating magnetic field. This speed difference is called slip. When load resistance increases, the rotor slows down and slip increases, resulting in greater torque. This characteristic enables the induction motor to automatically adjust the output power when the load changes greatly, and has good load adaptability.
In short, the working method of an induction motor is to use a rotating magnetic field to generate an induced current in the rotor, thereby generating torque and driving the load to rotate. This kind of motor has the advantages of simple structure, high reliability and stable operation. It is one of the main types of motors widely used in various industrial and civil fields.
 2024-08-30 16:01:40
Engineering
2024-08-30 16:01:40
Engineering
 2024-07-26 14:09:13
Engineering
2024-07-26 14:09:13
Engineering
 2024-07-18 09:42:00
Engineering
2024-07-18 09:42:00
Engineering