- +86 19149417743
- Zhengzhou, Henan Province, China
- Mon-fri: 8am - 7pm
Get a quote
A DC motor is an electric motor powered by a DC power source. Its working principle is based on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction and Ampere's law. When passed through a DC power source, current passes through the stator coils and rotor coils of the motor. In the stator coil, the current generates a magnetic field, while in the rotor coil, due to the interaction of the current and the magnetic field, a torque is generated, causing the motor to rotate.
An AC motor is an electric motor powered by AC power. Its working principle is based on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction and the Hall effect. When AC power passes through the stator coil of the motor, it generates an alternating magnetic field, which interacts with the magnetic field in the rotor coil to produce a rotational torque, causing the motor to rotate.
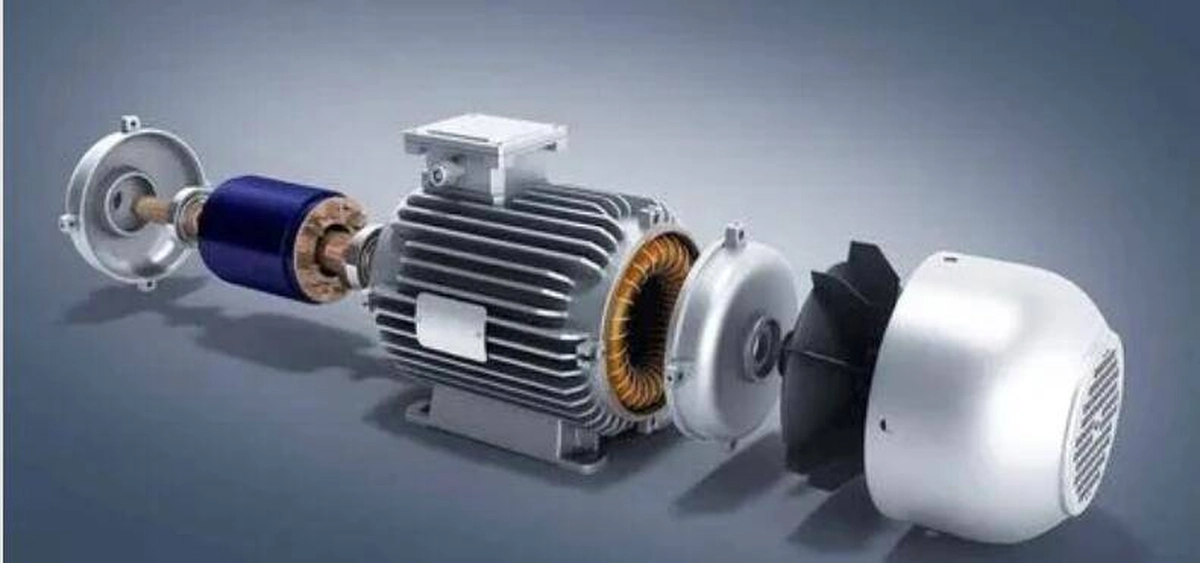
DC motors usually consist of stator, rotor, brushes, shaft and casing. The stator and rotor contain coils and magnets respectively. In a motor, the stator coil is fixed to the motor housing, while the rotor coil is mounted on the motor shaft. Brushes are used to connect the stator coil to an external power source in order to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.
The structure of an AC motor is relatively simple and usually consists of a stator, a rotor, a capacitor, a shaft and a housing. The stator and rotor also contain coils and magnets respectively. In AC motors, the rotor coil is usually made of aluminum and is connected to the stator coil through a capacitor.
DC motors are widely used in a variety of industrial and household devices such as fans, printers, power tools, and more. They have the characteristics of high efficiency, high torque, easy control of rotation speed, etc., so they are irreplaceable in many occasions.
AC motors are mainly used in household appliances, industrial equipment and other fields, such as electric fans, washing machines, compressors, etc. AC motors are widely used in household appliances due to their high efficiency and low noise.
As we all know, motors are the core component of household appliances. Everything from refrigerators to shavers need motors to drive them. Without motors, home appliances become just decorations. It is an electromagnetic device that realizes the conversion or transmission of electrical energy based on the law of electromagnetic induction. Motors can be divided into different types according to different division types. DC motors and AC motors are two common classification types. So, what is the difference between DC motor and AC motor?
In fact, the most fundamental difference between DC motors and AC motors is the type of power supply. One requires DC power and the other requires AC power. What follows is the difference in working principles and structural control. Let’s talk about it in detail next.
Because AC motors do not have carbon brushes and commutators, they do not produce sparks when the motor rotates. Therefore, they can be operated in high temperature, flammable and other environments, and there is no need to regularly clean the dirt on the carbon brushes.
Moreover, AC motors have high working efficiency, no smoke, odor, no environmental pollution, and low noise.
Due to its series of advantages, it has been widely used in various aspects such as industrial and agricultural production, transportation, national defense, commercial and household appliances, and medical electrical equipment.
To sum up, the difference between DC motors and AC motors is mainly due to their different power supply types, which in turn results in differences in working principles and structures. In terms of application, AC motors are suitable for situations where the speed and steering requirements are not high, while DC motors are suitable for situations where the speed and steering requirements are high. At the same time, due to the complex control method of AC motors, their costs are relatively high.
 2024-08-30 16:01:40
Engineering
2024-08-30 16:01:40
Engineering
 2024-07-26 14:09:13
Engineering
2024-07-26 14:09:13
Engineering
 2024-07-18 09:42:00
Engineering
2024-07-18 09:42:00
Engineering